Build custom Slackbot LLM Agent
Writing AI Agent
∙
Dec 23, 2025
Repetitive questions waste time and money. In a 1,000-person company, employees spend 6 hours weekly answering the same questions, costing over $2M annually. A Slackbot powered by large language models (LLMs) can fix this by automating answers to common queries like "What’s the PTO policy?" or "How do I reset my VPN?" - delivering responses in just 3.2 seconds.
With tools like Slack SDK, LangChain, and vector databases, you can build a bot that connects directly to your documentation (e.g., Notion, Confluence). This ensures employees get fast, reliable answers without pinging internal experts. Whether you're in HR, IT, or operations, this guide walks you through how to set up, test, and deploy an LLM-powered Slackbot to streamline workflows and reduce support ticket volumes.
Key Benefits:
Automates 35% of repetitive questions
Reduces response times from hours to seconds
Frees up internal experts for complex tasks
Follow these steps to build your bot:
Choose an LLM provider (e.g., NVIDIA, IBM watsonx).
Set up Slack permissions and tools (e.g., Slack Bolt, LangChain).
Build and test the bot’s logic for seamless integration with your knowledge base.
Deploy securely with scalable infrastructure to handle high demand.
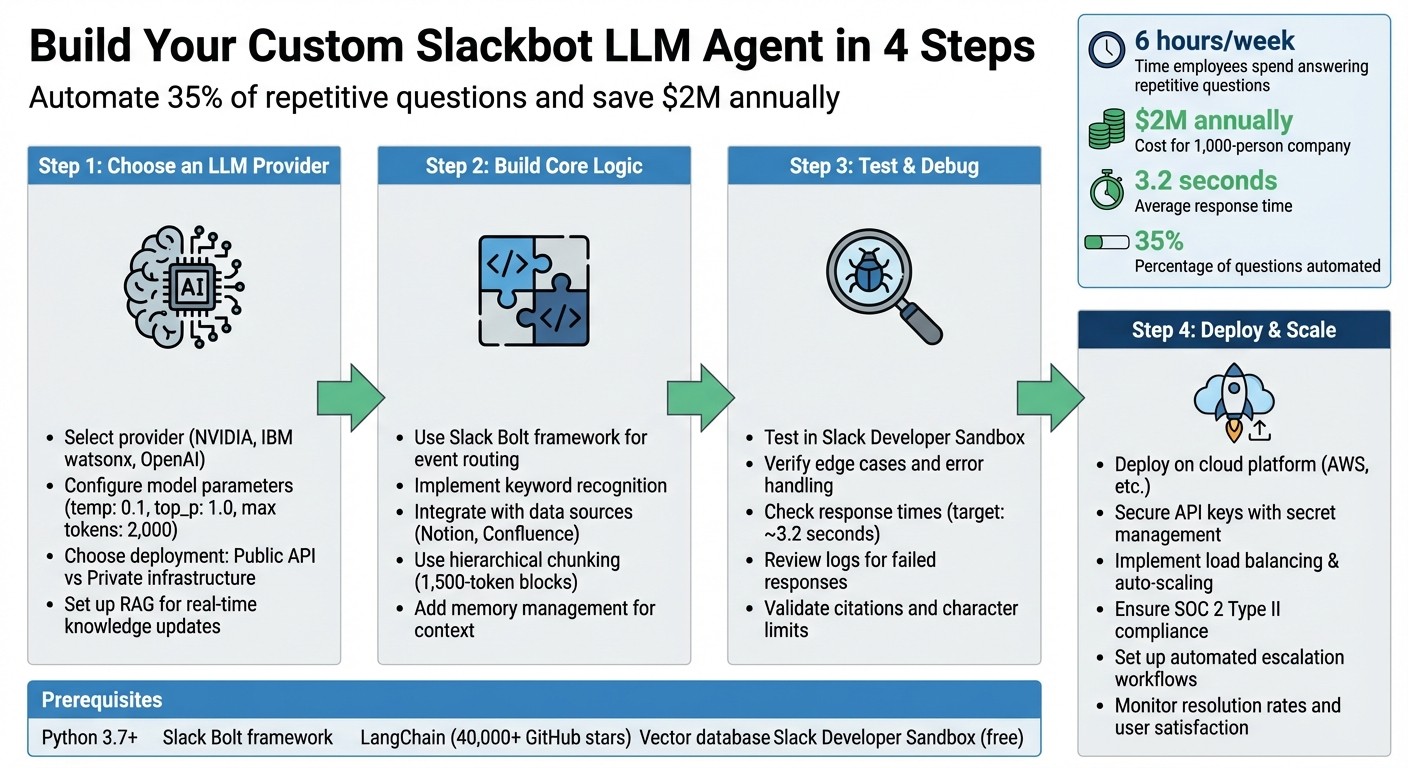
4-Step Guide to Building a Custom LLM-Powered Slackbot
Build a Slack AI Agent That Answers Questions (Step-by-Step Tutorial)
Prerequisites: Tools and Setup Requirements
Building a Slackbot powered by large language models (LLMs) requires specific tools and configurations. Fortunately, many of these resources are freely available, making it easy to prototype and test before scaling up to production. Here's what you'll need to get started.
Required Tools and Dependencies
To begin, you'll need Python 3.7 or later, which serves as the backbone for creating custom Slackbot LLM agents[6]. Pair this with the Slack Bolt framework, an official SDK designed for event routing and authentication within Slack apps[7][9]. Additionally, you'll rely on LangChain for managing interactions between LLMs, vector databases, and embedding models. As of May 2023, LangChain has gained significant popularity with nearly 40,000 stars on GitHub[8].
For LLM providers, consider options like NVIDIA AI Endpoints (offering models such as Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct) or IBM watsonx (featuring models like slate-125m-english-rtrvr-v2)[6]. If you're implementing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), you'll need a vector database. Popular choices include OpenSearch, Milvus, or Zilliz Cloud, all of which offer free tiers for initial use[6].
You'll also need to install the following Python packages: slack-bolt, python-dotenv, langchain, langchain-community, langgraph, langchain-nvidia-ai-endpoints, langchain-ibm, and opensearch-py[6][8][10].
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Begin by creating a Slack Developer Sandbox workspace, a free and secure environment for building and testing your app without impacting production workflows[7][9]. Install the Slack CLI, available for macOS, Linux, or Windows, to set up projects and manage authenticated logins using the slack login command[7].
For Python development, create a virtual environment with python3 -m venv .venv[7][10]. Store sensitive credentials, such as API keys and tokens, in a .env file and use the dotenv package to load them securely[9][11]. You'll need to configure environment variables like NVIDIA_API_KEY, WATSONX_APIKEY, and your Slack tokens[6].
Enable Socket Mode for local development. This mode uses WebSockets to allow your bot to receive events without requiring a public HTTP endpoint[7][10]. As noted by the Kubiya Blog:
Using Socket Mode allows the Slackbot to use websockets for interaction; this is often not allowed in a corporate firewall[10].
Once these steps are complete, you're ready to register your Slack app.
Registering Your Slack App and Setting Permissions
Go to api.slack.com and create a new Slack app. In the app settings, enable "Socket Mode" and generate an App-Level Token with connections:write permissions to simplify local testing[7][11]. You'll need two types of tokens: a Bot User OAuth Token (xoxb-) for performing bot actions and an App-Level Token (xapp-) for Socket Mode connections[7][9]. Always keep these tokens secure.
Set up the necessary OAuth scopes before installing your app. Add Bot Token Scopes such as chat:write (for sending messages) and app_mentions:read (to handle mentions)[9][10]. Additionally, in the "App Home" settings, enable the option to "Allow users to send Slash commands and messages from the messages tab", which facilitates direct message testing[9][11]. These configurations ensure your Slackbot can interact effectively within Slack.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building the Slackbot
Step 1: Choose an LLM Provider and Configure the Model
Start by selecting a large language model (LLM) provider that fits your specific needs. For straightforward summarization tasks, models like Llama 3.2 are cost-effective. However, if you’re dealing with complex reasoning or integrating large knowledge bases, consider options like GPT-4o or Claude 3.5 Sonnet[3][5]. For projects requiring extensive documentation support, models with larger context windows, such as Claude 3.5 or Mixtral-8x22b, are better suited[5][4].
Next, configure the model parameters. For example, set the temperature to 0.1, top_p to 1.0, and the maximum tokens to around 2,000 to ensure outputs are concise and factual[13]. Use system prompts to guide the model's behavior, such as instructing it to "always return citations" or "respond briefly and politely"[5].
For enterprise use, decide whether to rely on public APIs like OpenAI for convenience or private infrastructure options like AWS Bedrock or NVIDIA NIM for greater security and control[13][5]. Always encrypt sensitive data, such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), before sending it to external providers[5]. Many modern setups favor Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) over traditional fine-tuning, as RAG allows real-time updates to knowledge without the expense or privacy concerns of retraining model weights[12][4].
Once your model is set up, you’re ready to move on to building the bot's core logic.
Step 2: Build the Core Slackbot Logic
To handle events and route messages, use the Slack Bolt framework to create the bot's core logic. Configure trigger-based responses by implementing keyword recognition[13], enabling the bot to respond intelligently based on the context of user queries.
Integrate the bot with your organization’s data sources to ensure it provides answers rooted in reliable documentation. Use hierarchical chunking, breaking content into 1,500-token parent blocks, so the model receives complete sections of information rather than fragmented snippets[4]. Eliminate unnecessary tokens like excessive emojis or long URLs from inputs to maximize the efficiency of the model's context window[12].
Incorporate memory management to maintain conversational context across exchanges. Validate outputs using tools like Pydantic to ensure consistent formatting[14]. For organizations prioritizing data privacy, consider deploying the bot locally with solutions like LocalGPT, keeping all data within your internal infrastructure[14].
Once the core logic is in place, thoroughly test and debug your Slackbot to ensure it performs as expected.
Step 3: Test and Debug Your Slackbot
With the logic and model settings integrated, test the bot in varied scenarios. Use your Slack Developer Sandbox to simulate user interactions and verify basic functions. Test edge cases, such as incomplete questions, ambiguous phrasing, or queries requiring escalation. Intentionally introduce failures, like API timeouts or malformed inputs, to evaluate how the bot handles errors.
Make sure responses stay within Slack’s character limits and that citations link correctly to their sources. If the bot interacts with multiple data systems, confirm it retrieves information from the right source based on the context of the query.
Use logging to track key performance metrics, such as response time and accuracy. Aim for response times similar to AI answer agents, which average about 3.2 seconds[1]. Regularly review logs to identify patterns in failed or incomplete responses, then refine system prompts or retrieval logic to address these gaps.
Step 4: Deploy Your Slackbot
Deploy the bot on your chosen cloud platform, ensuring all API keys and tokens are securely stored using secret management services instead of embedding them directly in your code.
Prepare the infrastructure to handle high traffic by implementing load balancing and auto-scaling. For enterprise-level deployments, ensure compliance with security standards like SOC 2 Type II. Use analytics tools to monitor the bot’s performance, tracking metrics such as resolution rates, automation rates, and user satisfaction.
Set up automated escalation workflows so that unanswered questions are routed to the appropriate human experts. This ensures employees still get accurate information when the bot encounters knowledge gaps. As your organization grows, scale your infrastructure to maintain consistent performance. Keep in mind that employees often spend 20–30% of their workweek searching for information[1], so a well-functioning bot can save significant time and improve productivity.
Optimizing and Scaling Your Slackbot
Track Performance and Pinpoint Knowledge Gaps
Keep a detailed log of every interaction. Use tools like Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL to store query data and DynamoDB to track conversational history[2]. Regularly monitor resolution rates and flag queries that exceed your bot's confidence threshold[2][4].
Establish a weekly review process to analyze unanswered questions. If you notice recurring topics that your bot struggles with, it’s a clear indicator of a knowledge gap. For example, in 2023, Benchling developed a Slackbot to handle Terraform Cloud questions. By reviewing queries requiring manual intervention, they identified patterns and updated their knowledge base accordingly. To keep information up-to-date, they automated weekly data syncs using CloudWatch cron jobs[4]. These insights, combined with the bot's core logic from earlier development steps, drive continuous improvements.
For teams that rely on verified documentation rather than chat logs, platforms like Question Base simplify the process with built-in tools for gap analysis and resolution tracking. While Slack AI can summarize past conversations, specialized solutions like answer agents directly connect to trusted sources such as Notion, Confluence, and Salesforce. This ensures responses are expert-verified and accurate[1]. In fact, organizations have reported that automating responses to repetitive questions saves internal experts over 6 hours per week, with 35% of such queries being handled automatically[1].
Fine-Tune Responses and Tailor Behavior
Once you’ve established your bot’s baseline performance, focus on refining its responses. Adjust the bot’s tone and accuracy by tweaking temperature settings. For precise, technical answers, set the temperature to 0.1. If a conversational tone is more appropriate, increase it slightly[2]. Use LangChain Hub templates to refine system prompts and experiment with variations to improve resolution rates[2].
Introduce custom triggers, such as hashtags, to route specific queries[2]. Extend LangChain’s BaseTool class to create tailored tools for various needs - one for FAQ retrieval, another for ticket creation, and a third for searching your knowledge base[2]. This level of customization allows your bot to handle HR inquiries differently from IT support, ensuring it meets the unique requirements of each department.
Run A/B tests on different prompt versions to measure user satisfaction. Adjust the max_tokens parameter to control the length of responses. Regularly review bot outputs alongside user feedback to identify areas for further improvement[2][3].
Build Infrastructure for High-Volume Demands
Once your bot delivers high-quality responses, shift your focus to scaling its infrastructure to handle increased usage. Deploy your bot on AWS using auto-scaling, horizontal container deployments, and caching to handle peak traffic seamlessly[2]. For extremely high query volumes, consider enterprise-scale solutions like NVIDIA NIM microservices or similar large language model (LLM) providers[2][3].
Set up load balancing to evenly distribute incoming requests across multiple bot instances. Implement API rate limiting to prevent resource exhaustion during traffic surges. Keep an eye on latency, and scale up when average response times approach 5 seconds[2].
For organizations managing sensitive information, prioritize security by ensuring SOC 2 Type II compliance and implementing role-based access controls. This allows different user groups to interact with tailored versions of the bot. For enterprises with over 1,000 employees, these measures are not just about efficiency - they address a pressing issue. Companies lose over $2M annually due to time wasted searching for information, making scalable and reliable Slackbots a smart operational investment[1].
Conclusion
Creating a custom Slackbot powered by large language models (LLMs) can redefine how your team manages internal support and accesses knowledge. This guide walked you through the essential steps: choosing an LLM provider, configuring Slack permissions, designing the bot’s core logic with LangChain, and deploying it effectively. Each phase contributes to building an intelligent assistant that streamlines repetitive tasks, retains institutional knowledge, and keeps your team moving efficiently.
The benefits are clear. Automating responses can significantly enhance productivity and cut down the time spent searching for answers.
Once your bot is up and running, here’s how to maximize its potential: Start with a specific use case, such as answering HR-related questions, resolving IT issues, or assisting with onboarding. Test the bot thoroughly before expanding its scope. As it evolves, consider integrating automated knowledge base updates and tracking its performance to fine-tune responses. For enterprise teams handling sensitive data, it’s crucial to prioritize SOC 2 compliance and implement role-based access controls from the beginning.
If building a custom bot feels too resource-intensive, platforms like Question Base offer a ready-to-go alternative. These enterprise-grade solutions connect directly to trusted tools like Notion, Confluence, and Salesforce, ensuring that responses are accurate and verified by experts. Unlike Slack AI, which primarily relies on chat history, these specialized answer agents deliver faster results with built-in features like analytics, duplicate detection, and knowledge gap tracking. For teams that need precision and scalability, this approach ensures reliable, audit-ready responses tailored to enterprise needs.
FAQs
How can a Slackbot powered by large language models (LLMs) enhance workplace productivity?
A Slackbot integrated with large language models (LLMs) can transform workplace efficiency by taking over repetitive tasks like answering frequently asked questions - all within Slack. It taps into expert-approved answers from reliable platforms such as Notion, Confluence, or Salesforce, eliminating the need for employees to hunt down information or repeatedly explain the same processes.
This setup frees up valuable time, keeps teams on the same page, and lets them concentrate on more impactful work. By simplifying knowledge sharing and ensuring reliable answers, an LLM-powered Slackbot boosts collaboration, streamlines workflows, and elevates team productivity.
What do I need to build a custom Slackbot powered by large language models (LLMs)?
To create a Slackbot powered by large language models (LLMs), you’ll need to bring together three essential components:
Slack integration: Start by using Slack’s Workflow Builder or API to establish how the bot interacts with users. This might involve setting up triggers like slash commands or specific keywords. You’ll also need to grant the bot permissions to access and respond within designated channels.
LLM with a RAG pipeline: Pair a large language model (such as OpenAI’s GPT) with a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework. This setup typically includes tools like LangChain for orchestration, a vector database for quick document retrieval, and an embedding model to convert your data into a format that’s easy to search.
Enterprise knowledge sources: Link the bot to trusted platforms your team already uses, such as Notion, Confluence, Salesforce, or Google Drive. This ensures that responses are pulled from reliable, expert-approved information rather than relying solely on Slack’s chat history.
By integrating these components, you’ll have a Slackbot capable of delivering accurate, context-aware answers tailored to your organization’s unique needs.
How can I make sure my Slackbot is secure and scalable for enterprise use?
Ensuring your Slackbot is secure and ready to grow with your team starts by choosing a platform built for enterprise-level demands. Question Base meets these expectations with its SOC 2 Type II certification, robust encryption for data both in transit and at rest, and detailed role-based access controls. These features allow you to precisely manage who can access or update your knowledge base, ensuring compliance and maintaining a clear audit trail. With built-in audit logs, you can track exactly who accessed specific information - an essential feature for industries with strict regulations.
Scalability is a key strength of Question Base, making it ideal for enterprises with thousands of employees. It efficiently handles large volumes of questions thanks to tools like duplicate detection, per-channel customization, and AI-powered learning that identifies and addresses knowledge gaps. The platform’s analytics dashboard provides insights into resolution rates and automation performance, helping you fine-tune operations as your needs expand. Additionally, its cloud-native design ensures automatic load balancing and scaling, eliminating the need for manual server management.
While Slack AI excels at general productivity tasks, such as summarizing conversations, its learning is largely limited to chat history. For teams that require verified, audit-ready answers pulled directly from trusted systems like Notion, Confluence, or Salesforce, Question Base offers a secure and scalable solution tailored to meet the demands of enterprise environments.
