Cross-Cloud Data Sync: Best Practices for Enterprises
Writing AI Agent
∙
Feb 6, 2026
Synchronizing data across cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud is complex but critical for modern enterprises. Without a clear strategy, businesses risk higher costs, data silos, and operational disruptions. This guide simplifies the process by focusing on secure methods, performance optimization, and cost-effective strategies for syncing data across clouds.
Key Highlights:
Start with clear goals: Define what success looks like - improving uptime, meeting compliance, or reducing latency.
Choose the right method: Use real-time Change Data Capture (CDC) for low-latency needs, event-driven setups for flexibility, or batch synchronization for cost savings.
Secure your data: Enforce AES-256 encryption, TLS 1.3, and role-based access to protect information during transfers.
Monitor performance: Use centralized tools to track latency, errors, and compliance issues across platforms.
By following these steps, businesses can ensure reliable data synchronization while keeping costs and risks in check.
Building a Multi-Cloud Data Transfer System with AWS S3 + GCP Cloud Storage (Step-by-Step Tutorial)
What to Consider Before Implementing Cross-Cloud Data Sync
Before diving into transferring data across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, it's crucial to define your business goals and evaluate your technical systems. A staggering 90% of technology leaders identify integration with existing systems as a major challenge[8]. Taking the time to understand your current setup can save you from headaches down the line.
Start by clarifying what success looks like for your organization. Is it about improving system availability during outages, meeting data residency requirements, or speeding up time-to-market? These goals will influence key decisions, such as how often to sync data or which storage class to use. For instance, if you’re syncing daily sales summaries for reporting purposes, periodic bulk transfers could be more cost-effective than constant API calls[4]. However, if the goal is replicating transaction data for a customer-facing app, real-time synchronization becomes a necessity. Once your objectives are clear, evaluate whether your cloud platforms can work together seamlessly.
Platform differences can impact planning. For example, Google Cloud VPCs function globally, while AWS VPCs are regional[9]. Such distinctions directly affect your network topology. It’s also important to check if your target cloud’s object storage supports the APIs you need. For instance, some providers don’t handle the get-object-tagging request via the Amazon S3 API[3]. Running performance benchmarks with tools like iperf can help confirm regional latency and bandwidth suitability[9]. Additionally, storage tiers differ: Azure Blob archive tiers require a restore process before transfer, while Google Cloud Storage archive tiers allow immediate access but charge retrieval fees[3]. Addressing these compatibility factors early ensures smoother operations.
Resilience should be part of your strategy from the start. Take Coke One North America, for example - they transitioned their SAP landscape to Google Cloud for 35,000 employees by using Change Data Capture (CDC) to replicate transactions into BigQuery. This approach maintained business continuity without relying on manual ETL processes[10]. Similarly, Oldcastle Infrastructure cut $360,000 in annual costs by replacing manual ETL scripts with automated connectors during their Snowflake migration[10].
Don’t overlook rollback planning, phased cutovers, and continuous validation. Instead of leaving validation as a final step, compare row counts and sample records throughout the process[10]. This proactive approach is especially important given that 42% of enterprises report delays or underperformance in AI projects due to poor data readiness[10]. By building a solid synchronization framework, you’ll not only protect current operations but also set the stage for future initiatives.
How to Secure Data During Synchronization
Protecting data during cross-cloud synchronization is a critical step in ensuring operational resilience. When data moves between platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, it faces risks at every stage - whether in transit, at rest, or during processing. Even a single unencrypted connection or poorly configured access control can leave sensitive information vulnerable to unauthorized access. The stakes are high: organizations lose an average of $13 million annually due to poor data quality, and 64% of CIOs report delaying innovation efforts because of regulatory compliance concerns[10]. To address these challenges, encryption and access control become essential pillars of a secure synchronization strategy.
Enforce Advanced Encryption Protocols
Encryption is the cornerstone of protecting data during synchronization. For data at rest, AES-256 provides a strong defense with its 256-bit key and multiple transformation rounds. When data is in transit, enforce TLS 1.3 for all API endpoints and HTTPS connections. As of February 2024, major cloud providers like AWS mandate TLS 1.2 or higher for service API endpoints[11]. To ensure compliance, use IAM policy condition keys, such as aws:SecureTransport, to reject unencrypted requests and enforce HTTPS-only communication[11].
"While AWS employs transparent encryption at various transit points, we strongly recommend incorporating encryption by design into your architecture." - AWS Security Blog[11]
For network-level protection, implement IPsec VPN tunnels for site-to-site connections or MACsec for dedicated circuits like AWS Direct Connect or Azure ExpressRoute. These methods provide hardware-based, high-speed encryption to secure data flows[11][13]. When using AES, opt for GCM (Galois/Counter Mode) instead of ECB mode. GCM offers both confidentiality and integrity checks, whereas ECB can expose patterns in encrypted data[12]. To enhance security further, consider client-side encryption through tools like the AWS Encryption SDK. This approach encrypts sensitive data locally before transmission, ensuring end-to-end protection[11].
Implement Role-Based Access Control and Audit Trails
Encryption alone isn’t enough - effective access control ensures only authorized users and systems can interact with data. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign workload identities to microservices instead of relying on shared credentials. This allows for precise authorization policies that define which services can access specific APIs or transfer data across cloud platforms[1]. Store sensitive synchronization credentials, such as HMAC keys or SAS tokens, in centralized secret managers to minimize the risk of exposure[3].
For hybrid environments, prioritize service-account-based filtering over network-tag-based filtering to tighten firewall controls[7]. Establish a unified identity framework across cloud platforms so systems can authenticate seamlessly without duplicating access management efforts[7]. Additionally, maintain comprehensive audit logs that document who accessed data, when, and from where. These logs are invaluable for compliance checks and incident investigations.
Conduct Regular Security and Compliance Testing
Regular testing is vital to identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring synchronization processes remain secure. Integrate validation steps into your workflow, such as running reconciliation reports to spot data inconsistencies between source and target systems[10]. Use staging environments to test schema changes and transformations in isolation before rolling them out. Pilot runs with small datasets can help uncover potential issues early on[10].
Monitor performance logs to detect anomalies in pipeline health or latency during synchronization[10]. If your organization operates in regulated sectors like finance or healthcare, verify that encryption modules meet FIPS 140-2 or FIPS 140-3 standards[12][13]. To further reduce risk, establish a key rotation policy to limit the impact of any single encryption key being compromised[12]. You might also consider double encryption - applying file-level encryption on top of disk-level volume encryption - to add an extra layer of protection against breaches[12][13].
Selecting the Right Synchronization Methods
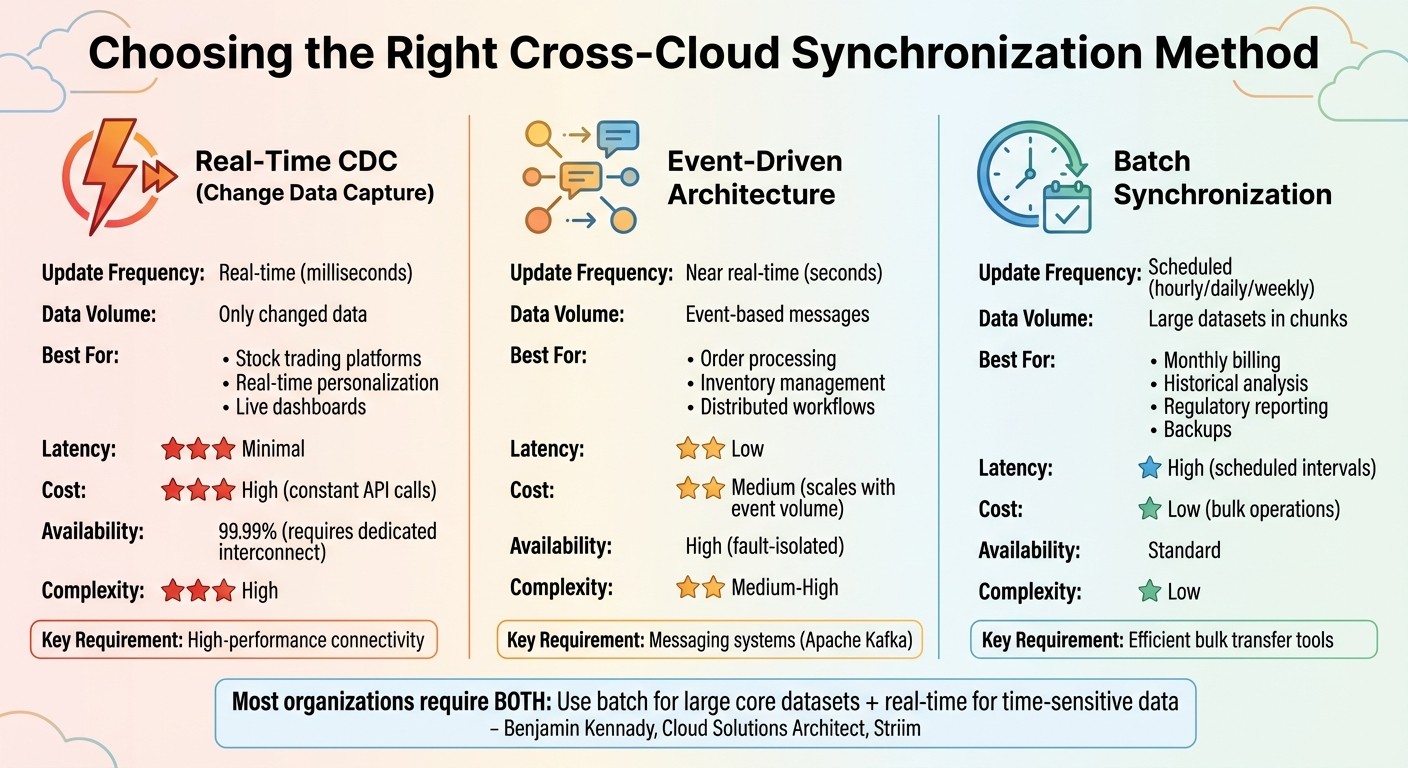
Cross-Cloud Data Synchronization Methods Comparison: CDC vs Event-Driven vs Batch
When it comes to secure data synchronization, the method you choose can make all the difference in ensuring your data is timely, cost-effective, and efficient. The right approach depends on factors like how quickly data needs to be updated, budget constraints, and the complexity of your operations. The three primary methods - real-time CDC, event-driven architectures, and batch synchronization - each serve distinct purposes.
Interestingly, the decision isn’t always a simple either/or choice. Benjamin Kennady, Cloud Solutions Architect at Striim, explains: "Batch will always have its place... Most organizations are going to require both." [15] Many enterprises adopt a hybrid strategy, leveraging batch synchronization for large, core datasets and using real-time methods for smaller, time-sensitive data. This mix helps balance costs and performance, allowing teams to allocate resources where they’re most impactful. Below, we’ll explore the key features and considerations of each synchronization method.
Real-Time Synchronization with Change Data Capture (CDC)
If your operations demand up-to-the-second updates, CDC is a powerful option. It tracks changes at the database level and syncs only the modified data, reducing the volume of data transferred between clouds. This makes it ideal for applications where latency is critical, such as stock trading platforms, real-time customer personalization, or dashboards that drive immediate decision-making [14].
However, implementing CDC across multiple cloud providers can be challenging. High-performance connectivity, like Cross-Cloud Interconnect or Dedicated Interconnect, is essential to maintain 99.99% availability and consistent throughput between platforms [1].
"Applications naturally perform best when they're located near their data. Moving applications away from their data sources creates unnecessary technical hurdles and slows performance." - AWS Prescriptive Guidance [4]
Before adopting CDC, evaluate each workload’s specific needs in terms of compute power, data operations, and latency [4]. Placing applications close to their primary data sources can help reduce network delays and improve overall performance [4]. Security is another critical factor; ensure end-to-end mutual Transport Layer Security (mTLS) and robust authorization policies are in place across service meshes [1]. While CDC offers the advantage of minimal latency, it also comes with higher costs due to constant API calls and connection overhead [14].
Event-Driven Architectures for Low-Latency Updates
Event-driven architectures rely on messaging systems like Apache Kafka, enabling services to communicate through events rather than direct API calls. This approach introduces loose coupling, which isolates systems so that issues in one cloud provider don’t cascade to others [5]. It’s especially effective for distributed systems that need immediate updates, such as order processing workflows or real-time inventory management across multiple warehouses.
"When organizations choose to distribute workloads across multiple clouds, adopting an architecture that's centered on messaging and loose coupling can alleviate many of the associated challenges." - AWS Prescriptive Guidance [5]
These architectures are well-suited for dynamic and rapidly changing datasets, but they can be complex to manage. Ensuring reliable message delivery and coordinating decoupled services require careful planning [16]. Costs scale based on the volume of events processed, offering more predictability than CDC but still higher expenses compared to batch processing [16]. To enhance security, use workload identity federation, which allows seamless authentication across cloud environments without juggling multiple sets of credentials [7].
Batch Synchronization for Cost-Efficiency
Batch synchronization is a more economical option, processing large datasets on a set schedule. While it introduces some latency, it offers high throughput and is ideal for non-urgent tasks like monthly billing, historical data analysis, regulatory reporting, or large-scale backups [15][16][14]. Data is collected over time and processed in chunks at intervals - hourly, daily, or weekly [15][16].
"Implement bulk data transfer between clouds instead of real-time access. Schedule periodic data refresh by using efficient bulk operations instead of using constant API calls between clouds. This approach reduces costs, improves reliability, and maintains consistent performance." - AWS Prescriptive Guidance [4]
To keep costs even lower, consider tools like AWS DataSync, which can compress data during transfers and significantly cut egress charges [3]. Before initiating synchronization, check whether the destination cloud supports object tags; if not, disable tag copying to avoid task failures [3]. For enterprises handling petabytes of data across platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, batch synchronization often strikes the best balance between performance, cost, and simplicity.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Maintaining top-notch performance across all clouds requires more than just secure synchronization methods - it hinges on continuous monitoring. Without a centralized system to capture team knowledge and oversee operations, issues like latency spikes, failed data transfers, or compliance lapses can easily slip through the cracks. Distributed cloud environments, in particular, bring unique integration challenges that demand a robust monitoring strategy [8]. A centralized view bridges synchronization efforts with operational oversight, ensuring nothing gets overlooked.
Use Centralized Monitoring and Governance Tools
Centralized monitoring tools are essential for tracking data flows, identifying errors, and ensuring compliance across multiple cloud providers. Solutions like Google's Network Intelligence Center offer a unified console for managing network visibility and troubleshooting distributed environments [7]. For API-driven synchronization, platforms such as Apigee provide real-time analytics, rate limiting, and security monitoring, making it easier to assess data exchange performance [7].
For enterprises juggling hybrid environments, Integration Platforms as a Service (iPaaS) tools are invaluable. These platforms consolidate data flow mapping between on-premises systems and various cloud services into a single dashboard [8]. To cut down on costs, synchronization agents that support data compression during transfers can help reduce outbound data expenses significantly [3].
Optimize Network Performance for Lower Latency
Latency is often dictated by physical distance - light travels through fiber optic cables at about 124 miles per millisecond [17]. For applications within a single country, central hubs can help balance latency [17]. When real-time synchronization is critical, Dedicated or Cross-Cloud Interconnects provide private, high-bandwidth paths between providers, offering more consistent performance compared to public internet connections [9].
Placing synchronization agents as close as possible to the source data is another effective way to minimize latency. For instance, deploying an Azure VM for Azure-based data ensures the agent operates within the same cloud environment, reducing delays [3]. For large-scale data, periodic bulk refreshes are often more reliable and cost-efficient than always-on real-time API connections, which can lead to higher operational costs [4]. To identify bottlenecks, monitor 95th and 99th percentile latencies, as these metrics provide a clearer picture of performance under peak loads [17]. These latency optimizations also tie into proactive alerting systems, helping maintain smooth operations during heavy usage periods. This is especially useful when teams need to automate internal questions during complex migrations.
Set Up Proactive Alerting and Auto-Scaling
Scaling performance requires a proactive approach. Deploying multiple agents to handle data transfers in parallel can significantly boost throughput [3]. Continuous monitoring is critical to prevent I/O overhead from slowing down your pipelines [2]. Tools like the Network Intelligence Center enhance visibility, allowing teams to catch potential issues before they escalate [7].
For simpler resource management and consistent monitoring, shared VPC networks are preferable to isolated setups [7]. If distributed clouds have overlapping IP address spaces, enabling Hybrid NAT on interconnects or VPN gateways ensures seamless routing [9]. By combining proactive alerting with auto-scaling capabilities, you can handle workload surges effectively and avoid synchronization bottlenecks that might disrupt operations. This strategy ensures your systems remain resilient under pressure and ready to meet demand.
Conclusion
Synchronizing data across clouds requires carefully balancing performance, security, and cost. One key principle: data gravity matters - placing applications near their data can help reduce latency and control expenses [4][6]. When planning your strategy, focus on keeping workloads close to their primary data sources and opt for bulk transfers instead of real-time API calls when dealing with large data volumes. This approach not only boosts reliability but also cuts costs significantly [4][5].
Equally critical is the architecture of your system. Effective design can be just as impactful as the technology itself. Aim for operational independence by incorporating messaging systems and loose coupling to avoid real-time dependencies between cloud providers [5]. This setup ensures that if one cloud environment experiences an outage, it won’t disrupt others. Additionally, deploying agents close to the source systems - such as within a source-cloud virtual machine - can help reduce both latency and egress costs [3].
Finally, cost awareness should influence every step of your plan. Verify compatibility thoroughly, as unsupported features like object tags can cause unexpected issues during transfers [3]. For high-availability connections, consider using redundant dedicated interconnects in different metropolitan areas to achieve uptime levels as high as 99.99% [1]. By balancing cost considerations with performance needs, you can lay the groundwork for a reliable and efficient data synchronization strategy.
FAQs
What challenges do enterprises face when syncing data across multiple cloud platforms?
Enterprises often face a tough time managing data across multiple cloud platforms. Each provider comes with its own set of APIs, interfaces, and security protocols, which can lead to errors, extra operational effort, and challenges in keeping data consistent.
One major hurdle is maintaining data integrity and synchronization without running into latency problems or surprise costs. Moving sensitive data between platforms introduces security and compliance risks, making robust encryption and strict access controls a must. On top of that, long-term integration planning is essential to avoid technical issues like mismatched workloads or conflicts with data residency requirements.
To tackle these obstacles, businesses need to focus on thoughtful planning, enforce strong security practices, and design efficient architectures. These steps are key to achieving smooth and dependable data synchronization across cloud environments.
What are the best ways to protect data during cross-cloud synchronization?
To safeguard data during cross-cloud synchronization, businesses need to focus on enterprise-grade encryption for both stored data and data in transit. Strengthening security measures with multi-factor authentication (MFA), maintaining strict access controls, and keeping a close eye on activity logs are critical steps to prevent unauthorized access. Regularly reviewing and updating security policies, along with conducting thorough audits, can further ensure alignment with industry standards and protect sensitive data across different platforms.
How do I decide between real-time, event-driven, and batch data synchronization methods?
Choosing the right data synchronization method depends on what you need in terms of update speed, complexity, and resource usage.
Real-time synchronization is the go-to option when immediate updates are non-negotiable. This is especially important for operational systems or workflows where instant consistency is a must. While it delivers updates with almost no delay, it can demand significant resources and be more challenging to manage.
Event-driven synchronization offers a middle ground by initiating updates only when specific changes occur. This approach works well for systems that need to react to events without the constant overhead of transferring data. It's a practical and efficient choice for scenarios with sporadic updates, providing scalability without unnecessary resource strain.
Batch synchronization is a better fit for situations where updates don’t need to happen right away, such as reporting or analytics. By grouping updates into scheduled intervals, this method simplifies processes and reduces costs. However, it does come with the trade-off of delayed data updates, making it better suited for managing large data volumes effectively.
The best choice depends on your priorities - whether that’s keeping data fresh, optimizing resource use, or managing costs effectively.