Evaluating Slack Apps for Enterprise Security Compliance
Writing AI Agent
∙
Feb 14, 2026
Third-party Slack apps can boost productivity, but they also introduce security risks. Apps often request unnecessary permissions, lack proper compliance certifications, or fail to meet key security standards. Without a structured review process, your organization risks exposing sensitive data and violating regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, or FINRA.
Here’s what you need to know:
Permissions: Apps may request broad access (e.g., private messages, file exports). Always apply the Principle of Least Privilege.
Compliance Gaps: Many apps lack certifications like SOC 2 Type II or clear data retention policies.
Visibility Issues: Unmonitored apps create blind spots, especially in large organizations.
Real-World Risks: Breaches like Disney’s Slack data leak (2024) show the dangers of unvetted integrations.
To stay secure, follow a checklist for setting up permissions, verify vendors’ practices, and enforce compliance standards. Tools like Question Base offer SOC 2 Type II compliance, verified AI responses, and granular access controls, making them a safer choice for enterprise Slack environments.
Slack DLP (Data Loss Prevention): How to protect Slack Workspace from security and compliance risks?
Security Risks of Third-Party Slack Apps
Third-party Slack apps can open the door to vulnerabilities in your workspace. These risks often arise from how apps request permissions, manage data, and function within your environment. Recognizing these potential threats is key to creating a safer integration strategy.
Overly Broad Permissions
A common issue with Slack apps is their tendency to request more permissions than they actually need, which increases the risk if the app is compromised. For instance, an app might ask for access to channels:history (to read all message history), files:read (to access all shared files), or even admin.* scopes [7]. If attackers gain control of such an app, they can exploit these permissions to access sensitive information.
Research shows that 43% of third-party apps in the Slack App Store have the ability to read messages in private chats [9]. This is alarming when you consider that the average employee shares 600 pieces of personally identifiable information (PII) in Slack - this includes an average of 478 email addresses and even 8 credit card numbers per user [7]. Apps with unrestricted read access put all this data at risk.
Real-world breaches highlight the severity of these risks. In July 2024, Disney experienced a major leak when the hacking group "NullBulge" stole 1.1 terabytes of internal Slack messages, exposing unreleased projects, source code, and login credentials [9]. Similarly, Rockstar Games lost 90 videos of unreleased Grand Theft Auto VI gameplay after a hacker exploited an employee's Slack account through social engineering [9]. These examples underline the importance of a thorough review process for app permissions.
Token misuse further compounds the problem. Researchers discovered 17,000 stolen Slack credentials from 12,000 workspaces being sold on the dark web. These tokens allow attackers to silently monitor private channels or impersonate legitimate users [7]. As Dvir Shimon Sasson, Director of Security Research at Reco, explains:
"OAuth Is Often the Weakest Link: Most Slack compromises stem from OAuth abuse - review every integration like you would a cloud IAM role." [8]
The issue goes beyond permissions. Many apps also fail to meet basic security benchmarks.
Failure to Meet Industry Standards
Beyond over-permissioning, many Slack apps fall short of meeting established security standards. While apps in the Slack Marketplace must pass a basic review process, this is a one-time evaluation that doesn’t include a full code audit [2]. Worse yet, apps distributed outside the official Marketplace face no review process at all [5].
This lack of consistency creates compliance headaches. Many apps lack certifications such as SOC 2 Type II and don’t provide clear data retention policies, putting regulated enterprises at risk. For industries bound by strict rules - like HIPAA in healthcare, FINRA in finance, or GDPR in Europe - using uncertified apps can lead to immediate violations.
SpinOne assigns risk scores to Slack apps, ranging from 1 to 100, with scores between 1 and 35 indicating high risk [10]. Without centralized governance, employees can install these high-risk apps without security team approval. Davit Asatryan, Vice President of Product at Spin.AI, warns:
"The reality with Slack is that once one user connects an application to Slack, all other users within the workspace are also able to utilize it. If there is no set process to inventory, assess and manage applications, organizations may face data leak and loss issues." [10]
AI-powered apps bring additional challenges. In August 2024, researchers demonstrated how indirect prompt injection could be used to extract data from private Slack channels, bypassing traditional access controls [9].
Poor Visibility and Monitoring
One of the most pressing challenges is the lack of visibility around app installations, their permissions, and who authorized them. Without proper oversight, unvetted apps can operate unchecked, creating security blind spots.
Unmonitored apps often retain outdated permissions or include collaborators who no longer need access. For example, an app installed for a short-term project might still have full access long after the project concludes, and former employees might retain access to company data through their personal accounts. Studies show that 74% of data breaches result from misconfigured permissions or weak access controls [9].
For large organizations, managing dozens - or even hundreds - of apps manually becomes nearly impossible. This challenge is compounded by Slack's lack of built-in tools for comprehensive app auditing on standard plans. As Slack itself acknowledges:
"You can't secure what you can't see. Regular auditing is critical for maintaining a secure app ecosystem." [4]
The September 2022 Uber breach is a stark example of how visibility gaps can lead to cascading failures. An attacker compromised a contractor’s Slack account using an MFA fatigue attack, then leveraged Slack access to infiltrate other systems like AWS and Google Workspace [9]. Even with monitoring in place, organizations face challenges like the "snapshot limitation" - security reviews only capture an app’s state at the time of submission, leaving room for risks introduced by later updates [2]. Continuous oversight is essential to address these gaps and ensure apps remain secure over time.
Compliance Standards for Slack Apps
When choosing Slack apps for enterprise use, it's crucial to have clear criteria to assess security and compliance. These benchmarks will depend on the sensitivity of your data, your industry, and any regulatory requirements your organization must meet. Given the risks involved, setting clear compliance standards is a must.
Required Certifications and Encryption
Start by checking the Slack Marketplace's Security & Compliance section for self-reported certifications, such as SOC 2 Type II. Keep in mind that Slack's review of app functionality is a one-time evaluation, so it's up to your team to verify ongoing compliance.
Ensure that apps encrypt data in transit using TLS and at rest with AES or similar encryption methods. They should also adhere to OWASP Top 10 security practices to mitigate common vulnerabilities.
Another critical factor is request signing, which ensures that incoming requests are genuinely from Slack. Additionally, look for apps that allow IP address restrictions for OAuth tokens, limiting their use to specific CIDR ranges. As Kurt Kemple, Senior Director of Developer Relations at Slack, points out:
"Apps on the Slack Marketplace must meet rigorous security requirements to protect your data, but apps not on the Slack Marketplace don't go through this process so we can't ensure their data security posture." [5]
Beyond these technical measures, make sure the app aligns with any regulatory standards specific to your industry.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Industries with strict regulations - such as healthcare, finance, or data privacy - require apps that comply with standards like HIPAA, GDPR, FINRA, or CCPA. While the Security & Compliance section of the Slack Marketplace lists these certifications, remember that this information is self-reported by developers.
Each app should have a publicly available privacy policy that outlines how data is collected, used, stored, and deleted. For GDPR and CCPA compliance, the policy must also explain how users can request data deletion. Apps dealing with highly sensitive information, such as health or financial data, might need to be custom-built internally rather than sourced directly from the Slack Marketplace.
For apps leveraging AI or large language models, developers should disclose details about data residency, tenancy, and whether Slack data is used to train their models. If this information isn’t readily available in the Marketplace listing, reach out to the vendor for compliance documentation, such as whitepapers or audit reports.
Authentication and Access Controls
Strong access controls are another layer of protection for your enterprise environment. Ensure that app permissions follow the Principle of Least Privilege, granting only the minimum access necessary. You might consider categorizing app scopes into groups such as:
Always Allowed: Low-risk permissions like basic commands.
Requires Approval: Medium-risk permissions like channels:history.
Restricted: High-risk permissions like admin-level access.
Enable the "Require App Approval" option in Slack’s App Management Settings so that your security team can vet all third-party tools before they’re installed. Assign dedicated App Managers to oversee this approval process.
Check that apps support features like automatic token rotation and manual revocation. Developers should avoid hardcoding credentials in production and instead rely on secrets management tools like AWS Secrets Manager or HashiCorp Vault. Additionally, apps that support Single Sign-On (SSO) allow you to centralize access control through your enterprise identity provider.
A great example of this approach comes from SoFi, which used Slack’s domain-wide authentication for the Google Calendar app in 2021. This enabled all 1,500+ employees to authenticate simultaneously, leading to a 790% increase in weekly active users within minutes of deployment [12]. As SoFi shared:
"While educating teams on how to use a new feature can take weeks, we were able to onboard thousands of employees to the Google Calendar app in a matter of minutes." [12]
How to Evaluate Slack Apps for Security
After defining your compliance standards, it's time to implement them. Evaluating Slack apps requires a careful balance between functionality and security. Here's a practical approach to determine if an app aligns with your enterprise needs.
Review App Permissions
Start by examining the app's requested scopes (permissions). A good rule of thumb is the Principle of Least Privilege - apps should only request the access they absolutely need. Kurt Kemple, Senior Director of Developer Relations at Slack, emphasizes:
"Every app should only have the minimum permissions (scopes) necessary to perform its function." [4]
Organize scopes by risk:
Low-risk scopes (e.g.,
commands,chat:write) can often be pre-approved.Medium-risk scopes (e.g.,
channels:history,users:read) usually need manual review.High-risk scopes (e.g.,
admin.*,search:read,files:read) typically require executive or security team approval [4][5].
By keeping permissions as minimal as possible, you reduce the likelihood of a security lapse.
To maintain control, enable the "Require App Approval" setting in your Slack admin dashboard. This ensures team members can't install unvetted apps without oversight [4]. For added efficiency, use the Slack CLI to generate a list of all installed apps and their scopes, making it easier to identify any that conflict with your internal policies [4][6].
For apps dealing with AI or sensitive data, scrutinize permissions even more closely. Slack performs enhanced reviews for scopes like files:read, canvases:read, and conversations.connect:write to ensure these apps meet higher security standards [1].
Once permissions are reviewed, focus on the vendor's security practices.
Check Vendor Security Practices
The Security & Compliance tab on each Slack Marketplace listing is a good starting point. Here, you'll find self-certified details about the vendor's data handling policies, certifications, and security measures [2][3]. However, keep in mind that Slack's security review is a one-time evaluation, not a continuous certification process [13].
To dig deeper, request documentation such as SOC 2 Type II audit reports and penetration test results [2]. Ensure the vendor adheres to industry standards, including testing for vulnerabilities like XSS, CSRF, and SQL injection, which are part of the OWASP Top 10 [13][14]. Slack clarifies:
"The Slack Application Security Review is not a certification, or proof of a secure application. Additional vulnerabilities may exist after a review, and we may revisit your application in the future to re-evaluate the security of your offering." [13]
Look for vendors that use request signing to verify communications originate from Slack. Additionally, check if they support IP address restrictions for OAuth tokens, which adds another layer of security [2][3][4]. Vendors should also respond to support inquiries within two business days, ensuring timely assistance [1].
Once satisfied with vendor security, turn your attention to how the app handles and retains data.
Verify Data Handling and Retention
Review the vendor's privacy policy to understand how they collect, use, retain, and delete data [1]. For AI-integrated apps, ask about the specific model used, data residency, and whether your Slack data is used for training purposes. Marketplace apps are prohibited from using your data for training [1].
Ensure that data is encrypted both in transit (e.g., with TLS) and at rest (e.g., with AES) [11][4]. Tokens should be tied to specific users, hidden from UI or error messages, and revoked immediately if the app is removed [4].
For reference, Slack itself deletes workspace-owner-initiated deletions from production systems within 24 hours, and service backups are typically destroyed within 14 days [11]. Third-party apps should follow similarly strict data deletion protocols to align with your enterprise security framework. This is especially critical for Slack backup in regulated industries where data retention is legally mandated.
How Question Base Meets Enterprise Security Requirements
Question Base vs Slack AI: Enterprise Security Features Comparison
When it comes to enterprise security, Question Base demonstrates how a purpose-built solution can address the rigorous demands of IT, HR, and operations teams. Designed with verified answers and enterprise-grade controls, it offers the tools organizations need to meet high security and compliance standards.
SOC 2 Type II Compliance and Encryption
Question Base is built to support SOC 2 Type II compliance, which ensures that its security controls are continuously effective [15][17]. As Stephanie Oyler from A-LIGN highlights:
"A SOC 2 report sends a signal to customers that your organization prioritizes IT risk, ethics, security, and the protection of their information." [17]
To protect data, Question Base uses encryption both in transit and at rest, adhering to industry standards [16]. For organizations with stricter requirements, on-premise deployment is available, offering full control over sensitive data. This level of security is particularly critical, given that the global average cost of a data breach is $4.45 million [19].
Controlled and Verified AI Responses
Question Base gives your team the power to manage AI responses by controlling, reviewing, and refining the content it accesses. You can specify trusted sources like Notion, Confluence, Google Drive, and Salesforce, ensuring employees only receive verified information. This aligns with expert recommendations for trustworthy AI usage. As Marcin Kapuściński explains:
"Trust in AI should be grounded in transparency, data quality, and auditability. Accurate AI decisions require a controlled, explainable environment." [18]
The platform also tracks unanswered questions and provides analytics on automation rates and resolution metrics. These features help identify knowledge gaps and ensure ongoing accuracy, which is especially important in compliance-heavy environments where every answer must be auditable. Unlike Slack AI, which relies on chat history, Question Base delivers responses directly from approved documentation.
Question Base vs. Slack AI
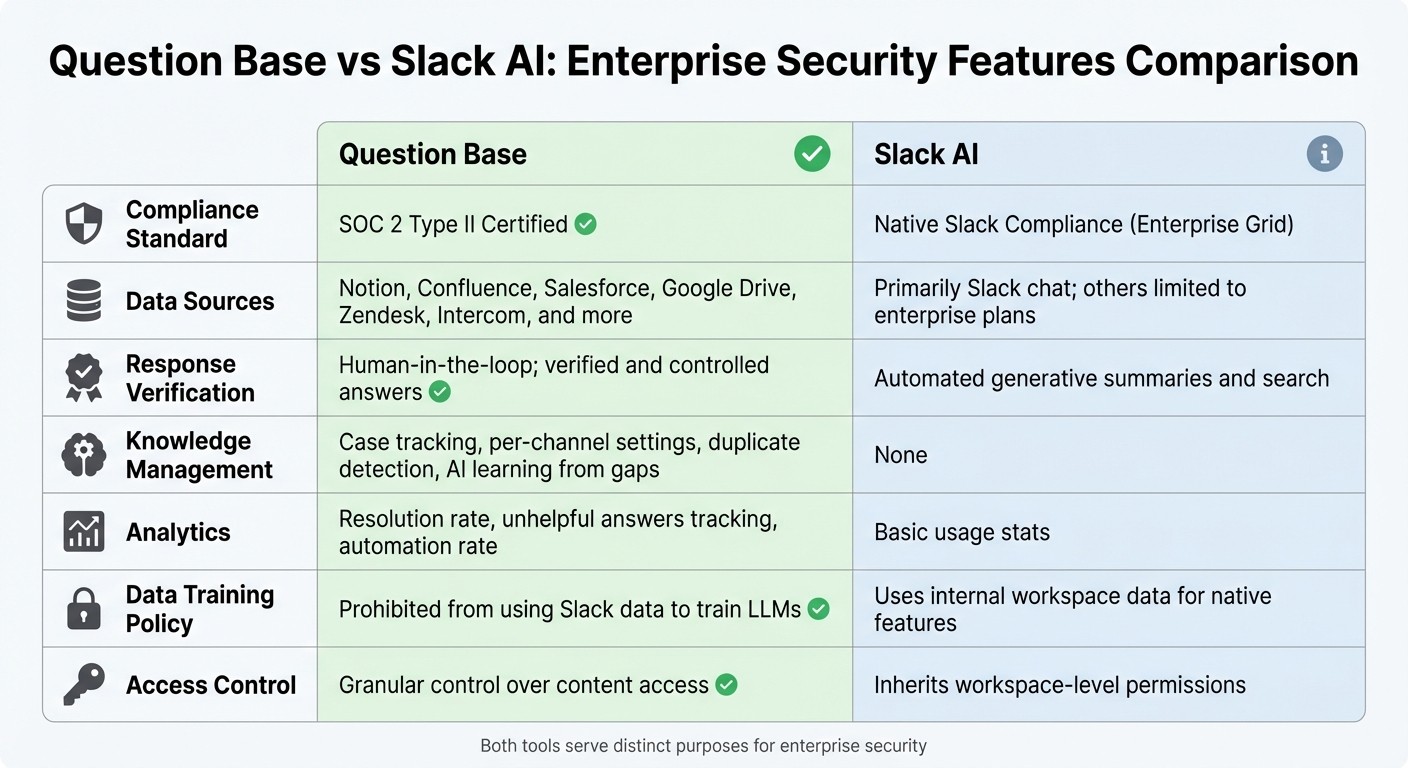
While Slack AI is a valuable tool for general productivity, Question Base offers a more tailored approach for teams that require verified, accurate knowledge at scale. Here's a side-by-side comparison:
Feature | Question Base | Slack AI |
|---|---|---|
Compliance Standard | SOC 2 Type II Certified | Native Slack Compliance (Enterprise Grid) |
Data Sources | Notion, Confluence, Salesforce, Google Drive, Zendesk, Intercom, and more | Primarily Slack chat; others limited to enterprise plans |
Response Verification | Human-in-the-loop; verified and controlled answers | Automated generative summaries and search |
Knowledge Management | Case tracking, per-channel settings, duplicate detection, AI learning from gaps | None |
Analytics | Resolution rate, unhelpful answers tracking, automation rate | Basic usage stats |
Data Training Policy | Prohibited from using Slack data to train LLMs [1] | Uses internal workspace data for native features |
Access Control | Granular control over content access | Inherits workspace-level permissions |
Both tools serve distinct purposes. Slack AI excels at summarizing past conversations, helping individuals work faster. Question Base, on the other hand, focuses on operationalizing knowledge for the future - ensuring accuracy, compliance, and expert oversight at every step.
Conclusion
Ensuring that Slack apps meet enterprise security compliance is an ongoing responsibility, essential for safeguarding your organization's data. As highlighted in Slack's Security Guide:
"Security shouldn't be an afterthought. A secure Slack ecosystem requires a proactive approach that integrates security principles directly into your development and management workflows." [4]
This proactive mindset involves robust governance and continuous monitoring. Key practices include enabling "Require App Approval", applying the principle of least privilege, and performing regular audits. These measures shift security from being reactive to becoming a core strategic function [4][3]. For AI-powered tools, it's crucial to demand clarity on how data is handled, where it is stored, and guarantees that Slack data won't be used to train large language models [1][5].
Purpose-built solutions like Question Base align with this framework, offering enterprise-grade security alongside practical functionality. Question Base provides SOC 2 Type II compliance, encryption both at rest and in transit, and optional on-premise deployment. It also delivers features such as verified AI responses, knowledge gap tracking, and seamless integrations with trusted documentation sources. Unlike generic AI tools that rely on summarizing past conversations, Question Base connects directly to your verified documentation, ensuring responses are accurate, traceable, and compliant.
The main takeaway: security compliance and operational efficiency can go hand in hand. By choosing apps that meet stringent security requirements while solving business challenges, organizations can expand their Slack ecosystem without sacrificing security. With approval workflows and transparent vendors, security becomes a strategic asset rather than a hurdle.
FAQs
What are the highest risk Slack app permissions?
The Slack app permissions that pose the greatest risk are those providing extensive access to workspace data. These include permissions for admin, identity, search, history, workflow steps, and trigger scopes. If misused, they can expose sensitive information or enable actions that could compromise the workspace.
How can we verify an app’s compliance claims?
To confirm an app’s compliance claims, examine how well it aligns with established security standards and policies. For instance, Slack scrutinizes apps in its Marketplace through security scans, manual reviews, and evaluations against guidelines such as least-privilege access and secure credential management. Additionally, tools like SpinOne can help assess app risks and compliance across various workspaces. A thorough approach that combines automated scans, manual inspections, and detailed developer documentation provides a more reliable verification process.
What’s a lightweight process to approve and monitor apps?
A streamlined approach starts with establishing clear guidelines and leveraging Slack's built-in app management features. For Enterprise plans, admins can set up approval workflows, allowing users to request apps while designated reviewers handle approvals. Admins also have the ability to track app usage, limit access, and revoke permissions as needed. By combining these approval workflows with regular monitoring, teams can ensure that only reliable apps are in use, maintaining both security and compliance with minimal hands-on management.
