Validating Slack Data Exchange: Key Steps
Writing AI Agent
∙
Jan 6, 2026
When your app interacts with Slack, verifying the authenticity of incoming requests is non-negotiable. Without proper validation, your system could fall victim to spoofed requests or replay attacks, jeopardizing sensitive workspace data. Slack uses HMAC SHA256 signatures to ensure secure data exchange, replacing older verification tokens. Here's how you can implement this process step-by-step:
Headers to Check: Every Slack request includes
X-Slack-SignatureandX-Slack-Request-Timestamp. Use these to validate the request.Timestamp Validation: Reject requests older than 5 minutes to block replay attacks.
Raw Request Body: Use the unaltered payload for signature calculations.
Signature Base String: Combine the version (
v0), timestamp, and raw body into a single string.HMAC Hashing: Compute the hash using your app’s Signing Secret and compare it securely with Slack's signature.
Skipping these steps leaves your app open to risks like unauthorized actions or compromised data. By following this guide, you can ensure every request is legitimate and safeguard your Slack integrations by following Slack security best practices.
Build your first Slack Bolt App Pt 3: OAuth & Storing User Credentials (w/ MongoDB)
Prerequisites for Slack Data Validation
To ensure successful Slack data validation and avoid signature mismatches, you'll need to gather a few key components and properly configure your backend.
What Is the Slack Signing Secret?
The Signing Secret is a unique UTF-8 string generated specifically for your app. Both Slack and your backend use this secret to create and verify request signatures, ensuring secure communication between them.
You can find your Signing Secret in the Slack App Management dashboard under the Basic Info section. Slack's documentation explains the process as follows:
"The signature is created by hashing the request body with the SHA-256 function, and combining it with an HMAC signing secret. The resulting signature is unique to each request and doesn't contain any secret information, keeping your app secure." [1]
If your Signing Secret is ever compromised, you can regenerate it through the admin panel and update your backend with the new secret.
Configure Your Backend for Validation
For proper validation, your backend must access the raw, unparsed request body. Parsing the request body before validation will result in signature mismatches.
In Node.js, for instance, you can use express.raw() to handle Slack endpoints correctly. Most programming languages provide built-in libraries to support HMAC SHA256 hashing, such as crypto in Node.js, hmac in Python, or similar libraries in Java.
Every incoming request from Slack includes the headers X-Slack-Signature and X-Slack-Request-Timestamp. These headers are case-insensitive, so variations like x-slack-signature should be treated the same [2].
Set Up Environment Variables
To manage your Signing Secret securely, store it as an environment variable named SLACK_SIGNING_SECRET. Additionally, set up another variable for the timestamp tolerance, such as SLACK_TIMESTAMP_TOLERANCE. This tolerance defines the maximum allowable time difference between the X-Slack-Request-Timestamp and your server's current time to protect against replay attacks. A 5-minute window (300 seconds) is the recommended standard [1][2].
Here’s an overview of the essential components:
Component | Requirement | Source/Location |
|---|---|---|
Signing Secret | Unique UTF-8 string | App Admin Panel > Basic Info |
Signature Header |
| Included in every Slack HTTP request |
Timestamp Header |
| Included in every Slack HTTP request |
Hashing Algorithm | HMAC SHA256 | Available in most standard libraries |
Tolerance Window | 5 minutes (300 seconds) | Best practice for replay protection |
Using the Slack Bolt Framework
If you're working with the Slack Bolt framework (available for JavaScript, Python, and Java), the framework simplifies this process. When you provide the SLACK_SIGNING_SECRET during initialization, it automatically handles signature verification. This built-in functionality reduces the chance of errors and saves development time.
How to Validate Slack Data Exchange
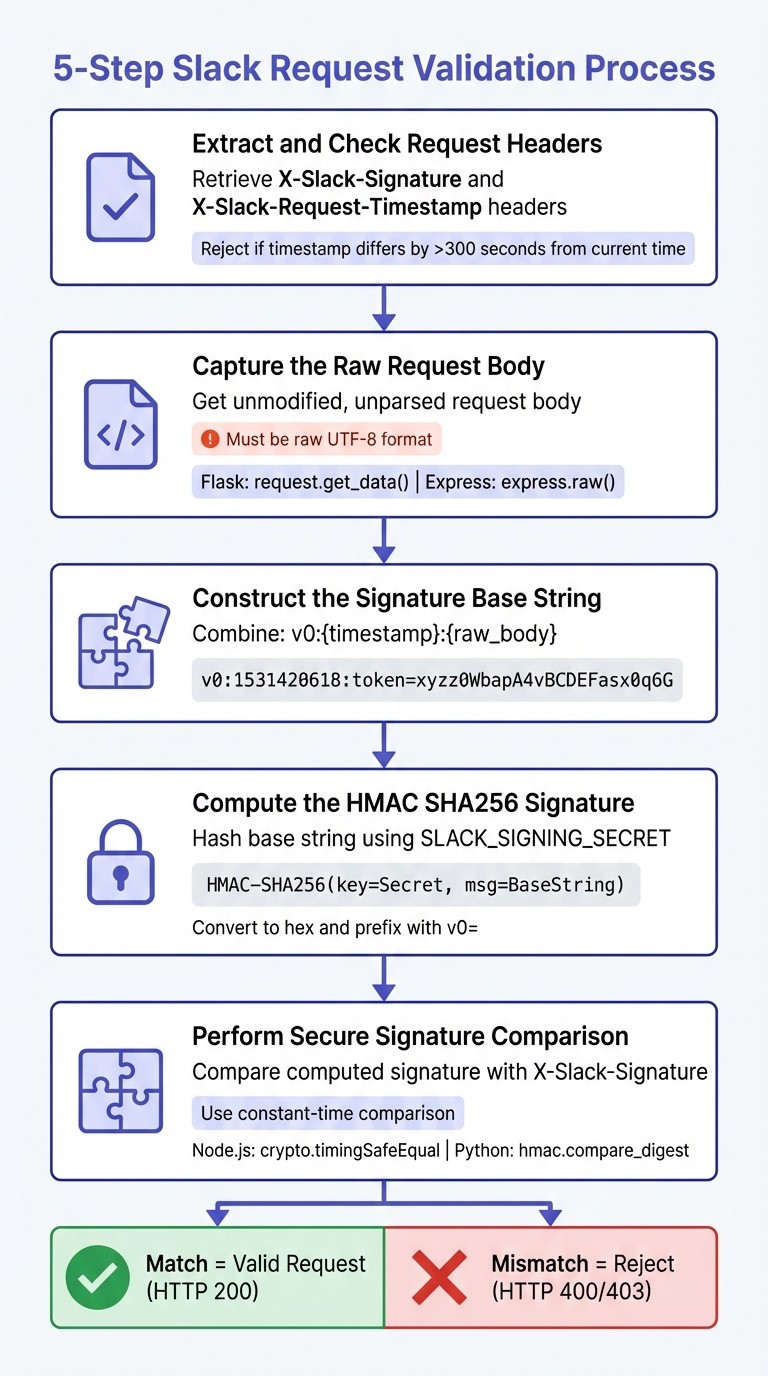
5-Step Slack Request Validation Process Using HMAC SHA256
Follow these steps to ensure secure communication between Slack and your backend system.
Step 1: Extract and Check Request Headers
Begin by retrieving the X-Slack-Signature and X-Slack-Request-Timestamp headers from the incoming request. These headers are critical for verifying the authenticity of the request.
Next, validate the timestamp to guard against replay attacks. If the difference between the timestamp and your server's current Unix time exceeds 300 seconds, reject the request outright. This time limit helps prevent malicious reuse of old requests.
Step 2: Capture the Raw Request Body
To validate Slack's signature, you must use the exact raw request body as it was sent - before any parsing or modifications. Altering the body, even slightly, will cause the signatures to fail.
For Python's Flask framework, use
request.get_data()to capture the raw payload.In Node.js with Express, configure
express.raw()for your Slack endpoints to ensure the body remains untouched.
Step 3: Construct the Signature Base String
Once you have the headers and raw body, it's time to create the signature base string. This string is a combination of three elements in the following format:
Here’s a quick example: if the timestamp is 1531420618 and the raw body is token=xyzz0WbapA4vBCDEFasx0q6G, the resulting base string will look like this:
The v0 at the beginning serves as a version identifier and delimiter.
Step 4: Compute the HMAC SHA256 Signature
Using your Slack Signing Secret (stored in the SLACK_SIGNING_SECRET environment variable), calculate the HMAC SHA256 hash of the signature base string. The resulting hash should be converted to a hexadecimal string and prefixed with v0= to match Slack's signature format.
Most programming languages provide built-in libraries for HMAC SHA256. For example:
In Node.js, use the
cryptomodule.In Python, leverage the
hmaclibrary.
Step 5: Perform a Secure Signature Comparison
Finally, compare your computed signature with the X-Slack-Signature header value. To prevent timing attacks, use a constant-time comparison function:
In Node.js, use
crypto.timingSafeEqual.In Python, use
hmac.compare_digest.
Avoid using standard string equality operators, as they can be vulnerable to timing attacks. A successful match confirms the request's authenticity.
Step | Action | Format/Component |
|---|---|---|
1 | Extract Header |
|
2 | Capture Body | Raw, unparsed UTF-8 request body |
3 | Create Base String |
|
4 | Compute Hash | HMAC-SHA256(key=Secret, msg=BaseString) |
5 | Format Final Signature |
|
6 | Compare Securely | Constant-time comparison with |
Handle Validation Failures and Errors
Once validation is complete, dealing with errors effectively is essential to keep your system secure. If validation fails, your backend must respond in a way that safeguards against risks like replay attacks, unauthorized access, and misconfigurations.
Reject Old Timestamps
After calculating the signature, check the X-Slack-Request-Timestamp against the current Unix time. If the timestamp differs by more than 300 seconds, reject the request. Make sure to log both the request's timestamp and your server's current time for debugging purposes.
Handle Signature Mismatches
When the computed signature doesn't align with the one provided, respond with an HTTP 400 or 403 status code. Log critical details, including the raw body, the provided signature, and the computed signature. To further strengthen security, validate the client certificate as an additional step.
Add Mutual TLS Verification
To enhance protection, configure your TLS-terminating server to require client certificates. Confirm that the certificate's Subject Alternative Name (SAN) or Subject Common Name (CN) matches platform-tls-client.slack.com. Accept requests only when this domain matches the expected value [1]. Additionally, ensure your application server verifies that the TLS-terminating server - not the client - added the verification header. Log the extracted SAN or CN to assist with troubleshooting certificate validation issues.
Failure Type | Detection Method | Response Code | Key Log Fields |
|---|---|---|---|
Old Timestamp |
| 400 or 403 |
|
Signature Mismatch | Computed hash ≠ | 400 or 403 |
|
mTLS Domain Mismatch | SAN/CN ≠ | 403 |
|
Test and Troubleshoot Slack Data Validation
Simulate Slack Requests
To ensure your implementation is solid, it’s crucial to simulate Slack requests during the testing phase. Start by using Slack's sample data to validate your setup before going live. For testing, use these specific values: the signing secret 8f742231b10e8888abcd99yyyzzz85a5 and timestamp 1531420618. These should produce the signature: v0=a2114d57b48eac39b9ad189dd8316235a7b4a8d21a10bd27519666489c69b503 [1].
If you're using Postman, make sure to include both the headers and a raw UTF-8 encoded body. Keep in mind that headers are case-insensitive, and the body must remain in its raw UTF-8 format.
For more advanced testing, leverage Slack's developer sandboxes. These provide a controlled environment to test platform features without impacting production systems. This is a key part of customizing Slack data flow for your team.
The outcomes of these simulated requests will guide how your validation process responds, as outlined below.
Validation Outcomes and Responses
Your backend should handle simulated requests with the following responses based on the validation results:
Valid signature: Respond with HTTP 200
Timestamp too old: Respond with HTTP 400
Signature mismatch: Respond with HTTP 400
Missing headers: Respond with HTTP 400
When debugging mismatched signatures, log the v0:timestamp:raw_body string to pinpoint issues. Always use constant-time comparison methods to protect against timing attacks. This ensures your validation process is both secure and reliable.
Conclusion
Ensuring secure data exchange in Slack is a joint effort between Slack and your development team. While Slack safeguards its infrastructure, it's up to you to implement robust validation measures to prevent request spoofing and protect the sensitive information flowing through your workspace. With reports of credentials for over 12,000 Slack workspaces appearing on dark web marketplaces and employees sharing an average of 600 pieces of personal data, the risks are far too significant to overlook this step [4][5].
The five-step validation process - extracting headers, verifying timestamps, constructing the signature base string, calculating the HMAC SHA256 signature, and securely comparing the results - serves as your frontline defense. By following this process, you can confirm the authenticity of requests and maintain data integrity.
Once implemented, make it a habit to rotate credentials regularly and maintain constant monitoring. Use the "Regenerate" button in your Slack App Admin panel to periodically update signing secrets, and integrate the Audit Logs API with your SIEM tools to detect unusual activity in real time [1].
For particularly sensitive data, consider adding extra layers of security. Techniques like Mutual TLS and official Slack SDKs such as Bolt can enhance protection. Always test these measures thoroughly in a developer sandbox before deploying them to production, and log signature failures to identify potential threats early.
As Slack aptly reminds us:
"Cybersecurity is a shared responsibility." - Slack [3]
FAQs
What happens if Slack requests aren’t properly validated?
If you don’t validate Slack requests, your app could face serious security threats like forged or harmful calls. This opens the door to unauthorized actions, data breaches, and the potential exposure of sensitive information. By validating requests, you ensure that only genuine communications from Slack are handled, safeguarding your app and its users.
How should I securely store and manage my Slack Signing Secret?
The Slack Signing Secret is a crucial piece of information that requires careful handling. To keep it safe, store it in a secure location, such as an environment variable or a specialized secret management tool. Avoid embedding it directly in your source code. Its primary purpose is to compute and verify the X-Slack-Signature for incoming requests, ensuring their authenticity. Under no circumstances should this secret be exposed publicly, as safeguarding it is essential to protect the integrity of your Slack integration.
How can I automate and validate data exchanges in Slack integrations?
Automating and validating data exchanges in Slack becomes much simpler when you leverage a mix of Slack’s built-in capabilities and external tools. Slack Workflow Builder is a no-code solution that lets you design workflows triggered by specific events, like a message or form submission. These workflows can integrate with external apps, such as Salesforce or Google Sheets, to automatically perform validation checks and maintain data accuracy.
For more complex automation needs, platforms like Zapier can step in to monitor Slack activities - like new messages or form responses - and trigger actions such as running validation scripts or updating records in other connected applications. Additionally, advanced tools like Functionize and Sigma Computing bring AI-powered data validation into the mix. When integrated with Slack using webhooks, these platforms can flag errors or enforce rules in real time, ensuring your data stays clean and compliant.
By combining Slack Workflow Builder with external automation tools and AI-driven validation platforms, you can build a dependable system that keeps your data accurate and reliable throughout the entire process.
