Why OAuth Matters for Slack Security
Writing AI Agent
∙
Jan 20, 2026
When you connect apps to Slack, you're granting them access to your workspace. OAuth 2.0 ensures this access is secure by verifying apps and limiting permissions to only what's necessary. It’s like giving a valet your car key but keeping the trunk and glove box locked. This safeguards sensitive company data while maintaining control over what apps can do.
Key Benefits of OAuth in Slack:
Scoped Permissions: Apps only access what they need (e.g., posting messages without reading history).
Token-Based Security: Temporary tokens replace passwords, expire every 12 hours, and can be revoked anytime.
User Transparency: Users see and approve requested permissions before granting access.
OAuth also prevents risks like token leaks, excessive app permissions, and unauthorized access by following Slack security best practices. By using secure token storage, HTTPS redirects, and IP restrictions, OAuth strengthens Slack integrations without compromising security.
For enterprises, OAuth ensures compliance and control, making it the backbone of secure Slack workflows.
How to OAuth with Slack using Node.js and Express
Security Benefits of OAuth for Slack
OAuth 2.0 strengthens Slack security by replacing broad permissions with precise, revocable controls. Let’s break down how OAuth enhances security through scoped access, token management, and clear user consent.
Scoped Access Control
Think of OAuth scopes as security clearances for apps. Instead of granting blanket access, you specify exactly what an app can do. For instance, an app might request the chat:write scope to post messages, but it won’t have permissions to read channel history, access user profiles, or perform administrative tasks [2]. Slack's OAuth v2 flow introduced more granular scopes, allowing apps to act independently through bot users instead of requiring excessive permissions tied to individual users [7]. This ensures apps only get the minimal permissions they truly need.
For example:
A simple slash command app might only need the
commandsscope.An integration that accesses message history would require
channels:history[2].
Organizations can organize these scopes by risk level to manage data access by role and streamline approval processes:
Low-risk scopes like
chat:writeorincoming-webhookcan be auto-approved.Higher-risk scopes, such as
channels:historyorusers:read, might trigger manual reviews.Critical scopes, including
adminoradmin.teams:write, require explicit administrative approval [2].
Token-Based Authorization
In addition to scoped controls, OAuth secures integrations with token-based authorization, which uses temporary credentials instead of passwords. Access tokens are issued through a secure handshake, ensuring safer authentication [7] [6]. Tokens are designed to expire every 12 hours, significantly reducing the risk of misuse [4]. When tokens expire, apps must use a refresh token to obtain new credentials. To prevent abuse, Slack enforces a limit of 2 active tokens when credentials are refreshed repeatedly before expiration [4].
Tokens can also be instantly revoked through the auth.revoke method - whether by users, administrators, or during app removal [7] [6]. To further secure token usage, organizations can configure up to 10 allowed IP address ranges. Any API call from an unauthorized IP will be rejected with an invalid_auth error, blocking token misuse from outside approved networks [2] [3].
User Consent and Transparency
OAuth ensures users have full visibility into what they’re authorizing. Before granting access, users see a transparent display of requested scopes [6]. This clarity helps users understand the permissions they’re approving. Additionally, OAuth includes safeguards against forgery attacks. For example, the state parameter - a unique string included in the authorization URL - must match upon Slack’s redirection back to the app. This prevents cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks, where bad actors might try to trick users into installing unauthorized apps [6].
For enterprise workspaces, administrators can enable "Require App Approval" settings. This feature ensures apps requesting high-risk scopes undergo manual review [2]. If a user denies a request during the OAuth flow, Slack sends an error=access_denied parameter back to the app, allowing it to handle the rejection gracefully instead of failing without feedback [6].
How OAuth Works in Slack Apps
OAuth plays a crucial role in ensuring Slack integrations are secure and efficient by combining scoped access with token-based authorization. Understanding this process reveals how it protects your Slack workspace while allowing knowledge management integrations for Slack to interact seamlessly.
The OAuth Flow for Slack Apps
Before an app can interact with Slack, developers must register it to receive a Client ID and Client Secret. These credentials serve as the app's identification during the authorization process.
The flow begins when the app redirects users to Slack's authorization URL: https://slack.com/oauth/v2/authorize. Here, the app specifies the required scopes - such as chat:write or channels:history - to define the permissions it needs. Users are then presented with a consent screen to approve or deny access. If they approve, Slack redirects them to the app's configured redirect URI, sending along a temporary authorization code. This code is only valid for 10 minutes [7][6].
The app's server then takes over by sending the temporary code, along with the Client ID and Client Secret, to Slack's token exchange endpoint: https://slack.com/api/oauth.v2.access. Once Slack verifies the credentials, it issues an access token. This could be a bot token (prefixed with xoxb) for app-level actions, or a user token (prefixed with xoxp) if user-specific scopes were requested [7]. The app uses these tokens to authenticate API requests by including them in the Authorization HTTP header: Authorization: Bearer xoxb-xxx [7].
For apps with token rotation enabled, access tokens expire every 12 hours [4]. When this happens, the app must use a refresh token to obtain new credentials. Slack limits apps to two active tokens if they are refreshed before the current token expires [4], reducing the risk of token misuse.
Slack-Specific OAuth Endpoints
Slack provides several endpoints to manage the OAuth lifecycle securely:
Authorization Endpoint:
slack.com/oauth/v2/authorizehandles user consent and scope requests.Token Exchange Endpoint:
slack.com/api/oauth.v2.accessconverts temporary authorization codes into access tokens.Legacy Token Upgrade:
slack.com/api/oauth.v2.exchangeupgrades older, long-lived tokens to expiring ones with refresh capabilities [4].Token Revocation:
slack.com/api/auth.revokeinvalidates tokens instantly, whether due to a security concern or app removal [4][7].
To maintain security, all redirect URIs must use HTTPS and exactly match the URL configured in the app's management settings. This ensures that authorization codes aren't sent to malicious sites [1][2]. Additionally, Slack verifies the state parameter during redirects to prevent CSRF attacks [1].
For organizations in the public sector using GovSlack, the authorization endpoint changes to https://slack-gov.com/oauth/v2/authorize [7]. This ensures compliance with stricter security and regulatory requirements.
Vulnerabilities That OAuth Prevents
OAuth Security Protections Against Common Slack Integration Vulnerabilities
OAuth offers a robust framework for addressing specific security risks in Slack integrations. Let’s break down the vulnerabilities it mitigates and how it keeps your workspace safer.
Common Slack Integration Risks
Integrating apps with Slack introduces several potential threats that could compromise sensitive company data. One of the most prominent risks is token leakage. This can happen when developers hardcode credentials into source code, accidentally commit them to public GitHub repositories, or expose them in error messages or user interfaces [3][2]. If a token is leaked, attackers gain direct access to your Slack workspace.
Another issue arises from excessive permissions. Older integrations often requested sweeping access across entire workspaces, even when they only needed limited functionality, like reading specific channels or posting messages. This "all-or-nothing" model meant that if an app was compromised, the attacker could access far more data than necessary [1][5]. The problem is compounded by long-lived credentials, which are static tokens that don’t expire, giving attackers an unlimited window to exploit stolen credentials [4].
During the OAuth flow, attackers may also attempt to intercept authorization codes, redirecting them to malicious sites [3][1]. For apps powered by AI, prompt injection attacks pose a newer threat. These attacks manipulate language models with malicious prompts, causing them to exfiltrate data to attacker-controlled URLs [3]. Such risks highlight the importance of stringent security measures.
How OAuth Prevents These Vulnerabilities
OAuth tackles these risks with a series of targeted defenses. For instance, token rotation ensures that access tokens expire after just 12 hours [4]. Slack also limits the number of active tokens to two per app during repeated credential refreshes, reducing the risk of token sprawl [4].
With granular scopes, apps are restricted to only the permissions they require. For example, an app might only need access to chat:write or channels:history, as specified in the manifest.json file. This ensures that even if an app is compromised, it can only interact with the data it was explicitly authorized to access [3][1].
OAuth also employs redirect URI validation, which ensures that authorization codes are only sent to HTTPS-secured domains that match the registered redirect URIs. This prevents attackers from intercepting codes during the OAuth flow [3][1].
IP address allowlisting adds another layer of security. Admins can restrict Web API token usage to a maximum of 10 specific IP address ranges or CIDR blocks [3]. If a token is leaked, any API calls originating from unauthorized networks will be rejected. Additionally, temporary authorization codes used during the OAuth flow expire within 10 minutes, making them nearly impossible to exploit if intercepted [1][6].
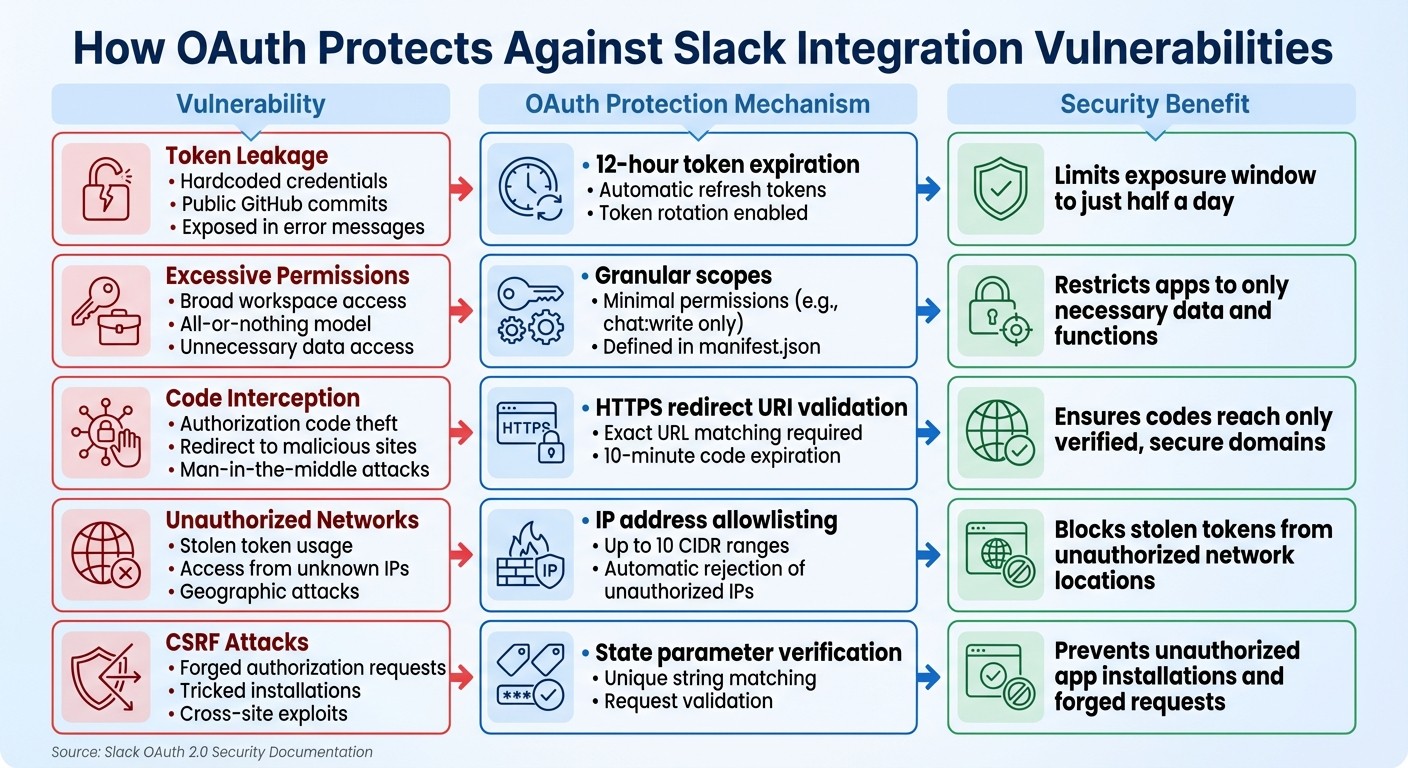
Here’s a quick overview of common vulnerabilities and the OAuth mechanisms designed to neutralize them:
Vulnerability | OAuth Protection | Security Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Token Leakage | 12-hour token expiration + refresh tokens | Limits exposure window to half a day [4] |
Excessive Permissions | Granular scopes (e.g., | |
Code Interception | HTTPS redirect URI validation | |
Unauthorized Networks | IP allowlisting (up to 10 ranges) | Blocks stolen tokens from unauthorized IPs [3] |
CSRF Attacks | State parameter verification |
OAuth’s layered protections are vital for safeguarding Slack integrations against both traditional and emerging threats. By addressing vulnerabilities like token leakage, excessive permissions, and code interception, OAuth ensures a more secure environment for your workspace.
Best Practices for Implementing OAuth in Slack
Building on OAuth's security advantages discussed earlier, these practices can help ensure your Slack integrations remain secure and efficient. Implementing OAuth effectively requires prioritizing security at every step. As Slack's documentation wisely notes:
"Security shouldn't be an afterthought. A secure Slack ecosystem requires a proactive approach that integrates security principles directly into your development and management workflows." [2]
Here’s how to keep your OAuth integrations both secure and functional.
Scope Minimization and Least Privilege
Only request the permissions your app absolutely needs. Slack's OAuth flow supports granular scopes, so you can, for instance, request chat:write to send messages without needing channels:history to read past conversations. Organize scopes by their risk level: low-risk (like commands), medium-risk (like channels:history), and high-risk (like admin) permissions [2].
Since scopes are additive and cannot be reduced once granted, it’s essential to define only the minimum permissions necessary from the start [6][7]. Include this minimal scope set in your manifest.json file. This approach forces you to carefully evaluate and justify any additional permissions during the development process.
Secure Token Management
Tokens and client secrets should never be hardcoded into your application. Instead, rely on secure environment variables and secrets managers. During development, use local environment variables (like .env files). For production, utilize tools such as AWS Secrets Manager or HashiCorp Vault to securely store secrets [2][3].
To further protect tokens:
Enable token rotation so that access tokens expire every 12 hours, with refresh tokens automatically renewing them [4].
Store tokens separately for each workspace and user to prevent cross-user exposure [2].
Immediately delete all associated tokens if a user removes the integration or deletes their account. This includes purging tokens from both production systems and backups [2].
These measures, combined with best practices for organizing Slack channels and proper redirect URI management, create a strong foundation for OAuth security.
Redirect URI Validation
Always use HTTPS-only redirect URIs that point to domains you control [2][7]. This ensures that authorization codes cannot be intercepted and sent to unauthorized third-party sites.
Incorporate a unique state parameter in your initial authorization request and validate it when the user returns. This step helps protect against Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attacks [6][7]. Authorization codes expire after ten minutes, so exchange them for access tokens promptly [1]. Additionally, limit Web API token usage to a maximum of 10 specific IP address ranges or CIDR blocks. Slack will automatically reject requests from any unapproved IP addresses [2][3].
Next, we’ll explore how enterprise tools like Question Base implement these practices to scale Slack integrations securely.
OAuth in Enterprise Tools: The Question Base Example
Question Base and Enterprise Security
When it comes to managing internal knowledge, enterprise tools must adhere to strict security protocols, and OAuth plays a critical role in achieving this. Question Base, an AI-powered answer agent that works seamlessly within Slack, demonstrates how OAuth ensures enterprise-grade security. This includes meeting SOC 2 Type II compliance standards while securely connecting to platforms like Notion, Confluence, Google Drive, and Salesforce.
Question Base showcases how these security protocols are implemented in real-world enterprise environments. By applying granular OAuth scopes, the platform requests only the permissions it needs - such as channels:history for accessing documentation or commands for handling inquiries. This approach aligns with the Principle of Least Privilege, ensuring that even if a token were compromised, the exposure would be limited to only what is essential for the app's functionality [1][2].
OAuth tokens are stored securely in encrypted databases hosted on AWS, with each token tied specifically to its corresponding workspace and user. The platform also leverages AWS Bedrock (Claude Sonnet 3.5), which avoids retaining any persistent input or output data, adding an extra layer of protection. All token transmissions are safeguarded using Transport Layer Security (TLS), ensuring that credentials are never transmitted without encryption [5][2].
These robust security measures allow Question Base to adapt OAuth practices effectively for large-scale enterprise use.
Scaling Secure Slack Integrations
Building on its strong token management foundation, Question Base extends its OAuth practices to meet the security demands of enterprise-scale operations. One key feature is its use of Slack's IP address restriction capability, which limits token usage to a maximum of 10 authorized CIDR ranges. This helps prevent unauthorized network access even in the event of a token leak [2][3].
Enterprise administrators can further enhance security by using Slack’s "Require App Approval" workflows. This feature allows them to review OAuth scopes before installation. Scopes are categorized into three levels: "Always allowed" (low-risk, such as commands), "Requires approval" (medium-risk, like channels:history), and "Restricted" (high-risk, such as administrative permissions). This centralized control ensures security practices remain scalable across the organization.
Additionally, Question Base takes proactive steps to manage token lifecycle events. When an employee leaves or an integration is removed, the platform uses Slack's auth.revoke method to immediately invalidate tokens and delete associated data. For compliance purposes, full deletion is finalized after a 35-day retention period [2][8].
These measures ensure that Question Base not only integrates securely into Slack but also scales its security practices to meet the needs of even the largest organizations.
Conclusion
OAuth has emerged as the cornerstone of secure Slack integrations for enterprise environments. By eliminating the risks of password sharing, enforcing precise access controls, and enabling centralized token revocation, OAuth tackles vulnerabilities that traditional authentication methods often overlook. The mid-2024 Disney breach - where attackers accessed 1.1 TB of internal Slack data due to overly broad access permissions - highlights the consequences of neglecting proactive governance in integrations [9].
As Slack itself has emphasized [2], security needs to be embedded into your ecosystem from the start. Tools like Question Base demonstrate how OAuth-compliant integrations can scale securely across large teams. By requesting only the permissions truly needed, encrypting token storage, and using features like IP restrictions and token rotation, these tools achieve SOC 2 Type II compliance while delivering immediate benefits to internal support workflows.
One of the most effective strategies is the move from long-lived credentials to expiring tokens that refresh every 12 hours, cutting the potential exposure window to just half a day if a token is compromised [4]. This approach not only limits risk but also strengthens administrative oversight. When paired with strict redirect URI validation and automated app approval workflows, OAuth allows enterprises to deploy integrations quickly without sacrificing control.
FAQs
How does OAuth 2.0 enhance security for Slack integrations?
OAuth 2.0 enhances the security of Slack integrations by implementing an authorization code flow. This approach ensures that apps exchange a short-lived code, safeguarded by a client secret, for access tokens. By doing so, it eliminates the need for apps to directly manage or store user passwords.
Moreover, OAuth enables apps to request only the permissions they actually require. This minimizes potential risks if a token is ever compromised. By restricting access scope and keeping sensitive credentials separate, OAuth plays a crucial role in safeguarding user data and maintaining organizational security within Slack integrations.
What are the advantages of using scoped permissions in Slack apps?
Scoped permissions, also known as OAuth scopes, enable Slack apps to request only the specific data and actions they require, rather than granting them unrestricted access. This approach aligns with the principle of least privilege, minimizing security risks in the event of a token compromise and supporting compliance with standards like SOC 2 Type II.
By specifying granular scopes, apps can function using their own bot identity without needing unnecessary, user-level permissions. This not only streamlines the installation process but also increases the chances of approval from workspace administrators. Additionally, when tokens are refreshed, they retain only the predefined access levels, further limiting potential vulnerabilities and enhancing overall security.
In practical terms, scoped permissions make security reviews more straightforward, provide clearer audit trails, and enable safer, more manageable integrations - key factors for enterprise-level Slack implementations.
How does token-based authorization enhance Slack security?
Token-based authorization ensures that apps can only access Slack data if they have valid tokens tied to specific permissions. Each API call requires one of these tokens, and access is restricted to the exact permissions the token grants. Token rotation and expiration provide an additional safeguard, allowing you to revoke or replace tokens whenever necessary. This helps to block unauthorized access if a token is ever compromised.
By using this method, you can protect sensitive data while ensuring that apps function strictly within the permissions you've set, maintaining the security of your Slack environment.
